How to Choose the Best Three Way Ball Valve for Your Industrial Needs
In the rapidly evolving industrial landscape, the importance of selecting the right components for fluid control cannot be overstated. Among these components, the three way ball valve has emerged as a critical element in various applications, offering versatility and efficient flow management. According to a recent industry report by MarketsandMarkets, the global ball valve market is projected to reach USD 10 billion by 2025, with a significant demand for three way ball valves driven by their ability to facilitate diverse operations in sectors like oil and gas, water treatment, and chemical processing. This growing trend underscores the necessity for industries to understand the nuances of choosing the best three way ball valve that aligns with specific operational needs while maximizing performance and reliability. As we delve into this guide, we will explore the key considerations and solutions available to help you make informed choices for your industrial needs.
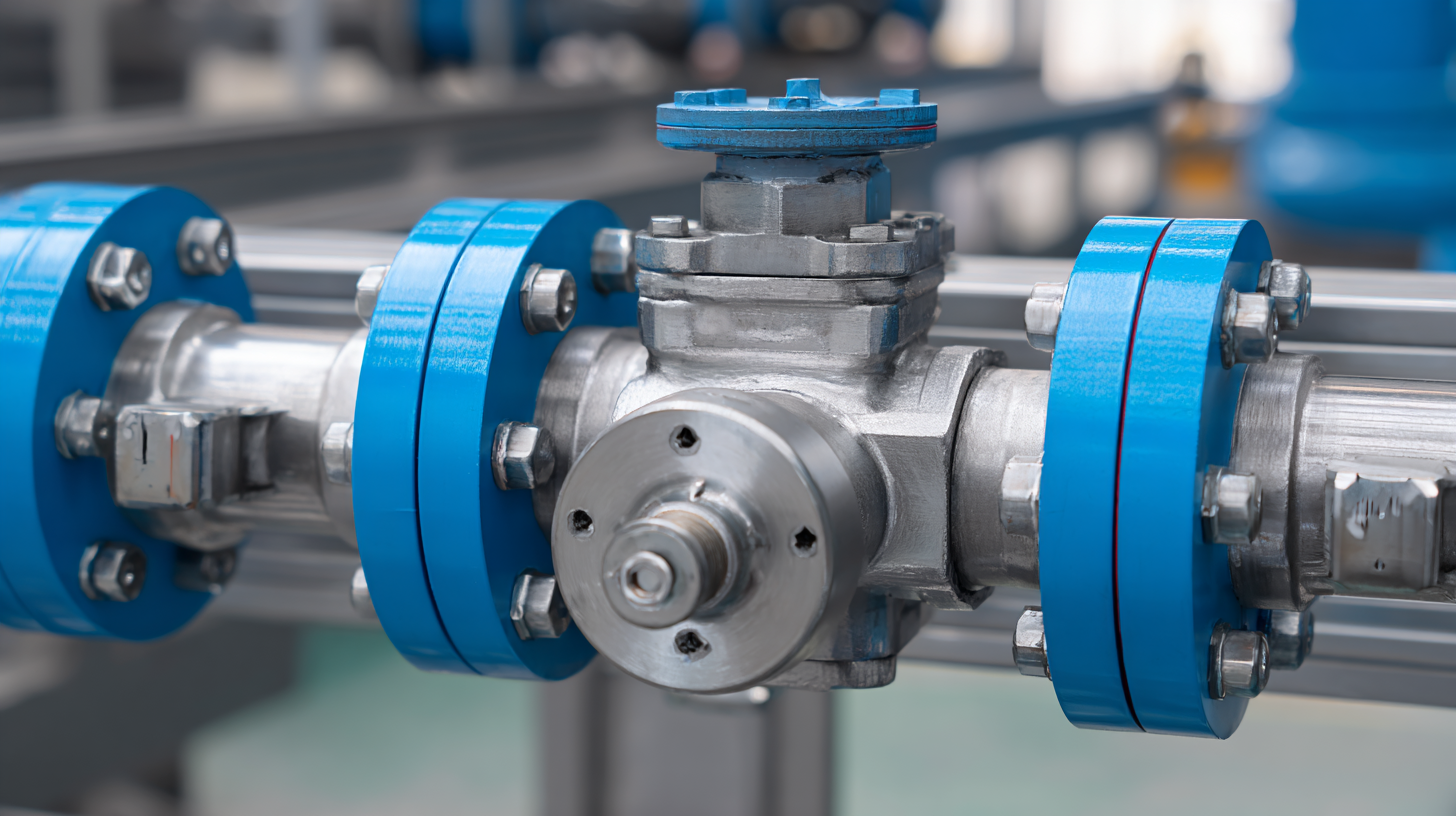
Understanding the Different Types of Three-Way Ball Valves for Industrial Applications
Three-way ball valves are essential components in many industrial applications, offering significant advantages in the control of fluid flows. Understanding the different types can help industries select the most suitable option for their specific needs. Generally, three-way ball valves come in two primary configurations: L-port and T-port. L-port valves are ideal for diverting flow from one path to another, while T-port valves can route flow to multiple directions, making them versatile solutions for complex systems.
According to a recent market report by MarketsandMarkets, the three-way ball valve market is projected to grow from $2.5 billion in 2023 to $3.2 billion by 2028, indicating a strong demand driven by various industries including oil and gas, water and wastewater treatment, and chemical manufacturing. Factors influencing this growth include the increasing need for efficient flow management and the rising preference for automation in valve operations. Additionally, industries are increasingly focusing on durability and material compatibility, with stainless steel being a popular choice due to its resistance to corrosion and high temperatures, enhancing the longevity of the valves in demanding environments. Understanding these nuances in valve types and their applications allows for better decision-making in the selection process.
How to Choose the Best Three Way Ball Valve for Your Industrial Needs
| Type of Valve |
Material |
Pressure Rating |
Temperature Range |
Applications |
| L-Port |
Carbon Steel |
150 PSI |
-20°C to 120°C |
Water, Oil |
| T-Port |
Stainless Steel |
300 PSI |
-40°C to 150°C |
Chemical Processing |
| Full Port |
Brass |
200 PSI |
-10°C to 140°C |
HVAC Systems |
| Reduced Port |
PVC |
100 PSI |
-10°C to 60°C |
Water Irrigation |
Key Factors to Consider When Selecting a Three-Way Ball Valve
When selecting a three-way ball valve for industrial applications, several key factors must be considered to ensure efficiency and reliability. First and foremost, the valve's size and flow capacity should be carefully evaluated. According to a recent report by the Global Valve Market, the demand for valves sized between 1 inch and 8 inches is projected to grow significantly, driven by increases in manufacturing and construction sectors. Choosing the correct valve size not only enhances flow performance but also minimizes pressure drop, thus optimizing operational efficiency.
Another critical factor is the valve material selection. The American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) recommends using materials such as stainless steel for high-corrosion environments or plastic for less demanding conditions. Statistics indicate that over 60% of valve failures in industrial settings are due to material incompatibility, which can lead to costly downtime. Finally, compatibility with control systems is vital; ensuring that the valve integrates seamlessly with existing infrastructure will streamline operations and improve control accuracy. By prioritizing these elements, industries can enhance productivity while minimizing risks associated with valve failure.
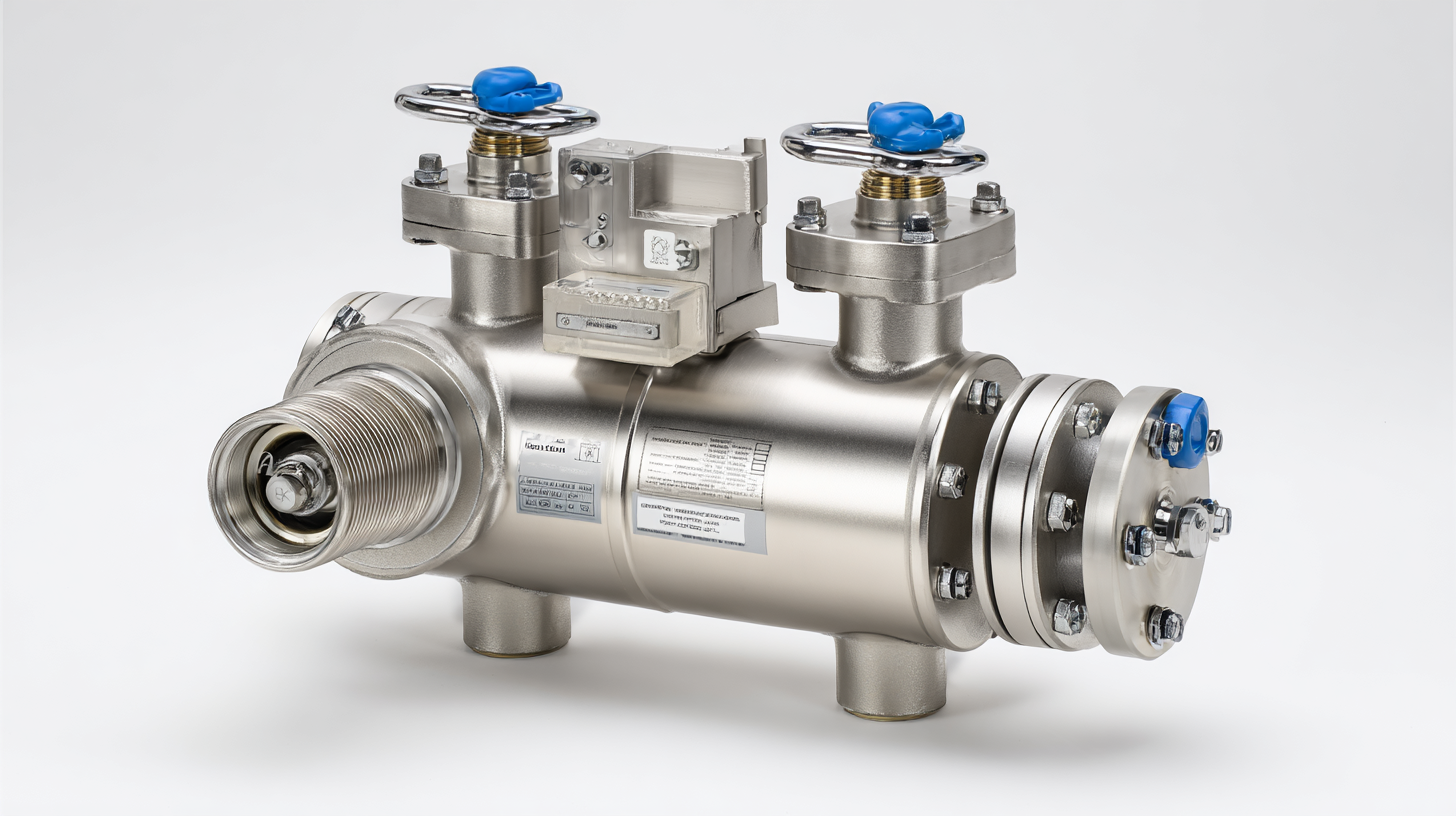

Advantages of Using Three-Way Ball Valves in Industrial Settings
Three-way ball valves have become essential in many industrial applications due to their versatility and efficiency. These valves allow for the diversion or mixing of fluids, which is particularly beneficial in processes requiring precise flow control. Their ability to handle varying pressures and temperatures makes them suitable for a range of industries, including oil and gas, chemical processing, and water treatment.
When selecting a three-way ball valve, consider the specific needs of your application. One crucial tip is to evaluate the valve's connection type—threaded, flanged, or welded—to ensure compatibility with your existing piping system. Additionally, pay attention to the materials used in construction. Opt for high-quality materials that can withstand the harsh conditions common in industrial settings to enhance durability and reduce maintenance needs.
Another important factor is the valve's actuation method. Manual, electric, or pneumatic actuators can significantly impact operational efficiency. Assess your workflow to determine the most suitable option for your facility. Choosing the right actuator can streamline processes and improve control over fluid movement, ultimately contributing to overall system efficiency.
Industry Standards and Certifications for Ball Valves: What You Need to Know
When selecting a
three-way ball valve
for industrial applications, adherence to
industry standards and certifications
is paramount. Recent market insights highlight that the global
ball valves market
size is projected to reach USD 22.5 billion
by 2033, growing at a
compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.7%.
This significant growth is driven by the increasing demand for
high-performance valves
across various sectors, including
smart mining
and
food processing industries.
As standards evolve, such as the new
68-01 guideline
regarding cleaning protocols in food processing, understanding the implications of these regulations on your choice of valves becomes critical.
Additionally, concerns over material safety have gained traction, especially regarding
brass ball valves. Recent reports note how the
lead leaching potential
from newly installed brass plumbing devices poses a risk, with levels exceeding
300 μg/L
in drinking water. This scrutiny underlines the importance of selecting valves that not only meet stringent quality standards but also carry the necessary certifications that affirm their safety and efficacy. With a proper understanding of these factors, you can ensure that your choice of
three-way ball valves
aligns with both regulatory compliance and operational excellence.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Choosing a Three-Way Ball Valve
When selecting a three-way ball valve for industrial applications, it's crucial to avoid common pitfalls that can lead to inefficiencies and increased costs. One of the most frequent mistakes is neglecting to assess the specific operational requirements of the system. For instance, according to a recent report by the International Journal of Valve Engineering, improper sizing can cause a loss of pressure and flow rates, resulting in up to 20% energy wastage. Understanding the flow direction and the intended application is essential for optimal performance.
Another common error is overlooking the material compatibility of the valve. Many industries face challenges with corrosive fluids that can damage improperly chosen materials. The American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) notes that using the right material can enhance the lifespan of a valve by up to 50%. Always consult material compatibility charts and consider the working environment to ensure durability and reliability.
Tips: Always perform a thorough analysis of your system's requirements before purchasing. This includes evaluating flow rates and pressures. Additionally, invest time in researching which materials best suit your specific application, ensuring that the valve will withstand operational stresses and minimize maintenance needs.

 © Copyright 2020 Tianjin Tanghaidongyang Valve Co., Ltd. All Rights Reserved.
© Copyright 2020 Tianjin Tanghaidongyang Valve Co., Ltd. All Rights Reserved.




